
Earlier this year the development of a new Street Design Standard for Moscow was completed under a large-scale urban renovation program entitled My Street, and represents the city's first document featuring a complex approach to ecology, retail, green space, transportation, and wider urban planning. The creators of the manual set themselves the goal of making the city safer and cleaner and, ultimately, improving the quality of life. In this exclusive interview, Strelka Magazine speaks to the Street Design Standard's project manager and Strelka KB architect Yekaterina Maleeva about the infamous green fences of Moscow, how Leningradskoe Highway is being made suitable for people once again, and what the document itself means for the future of the Russian capital.

Strelka Magazine: What is the Street Design Standard and what does it include?
Yekaterina Maleeva: The Street Design Standard is a manual for street planning in Moscow. The Standard is divided into four books, each one of them covering particular aspects of street design. Many cities across the globe have developed their own standards and the concept has gained a lot of popularity over the last decade. The New York Street Design Manual is a famous example; the book has even been translated into Russian. However, Moscow streets have little in common with New York streets, for example; every city has its own unique urban typology and simply copying existing solutions from another manual is not a viable option.
When we started our work on the Standard, the first thing we did was study Moscow streets, their peculiarities and common features. The first volume of the Standard focuses on the typology and distinctive attributes of the streets of Moscow. We gathered data on more than 3,000 streets and processed the data. Despite the large sample size, we discovered certain similarities. We managed to identify ten of the most common street types, but some unique streets could not be categorized. For instance, Tverskaya Street, built in 19th century, originally fell under category "10C." But after it was widened in the 1930s, Tverskaya ended up in a unique place within the urban fabric of Moscow. Such objects as that require a case by case approach and an individual project.
What can be found in the other volumes?
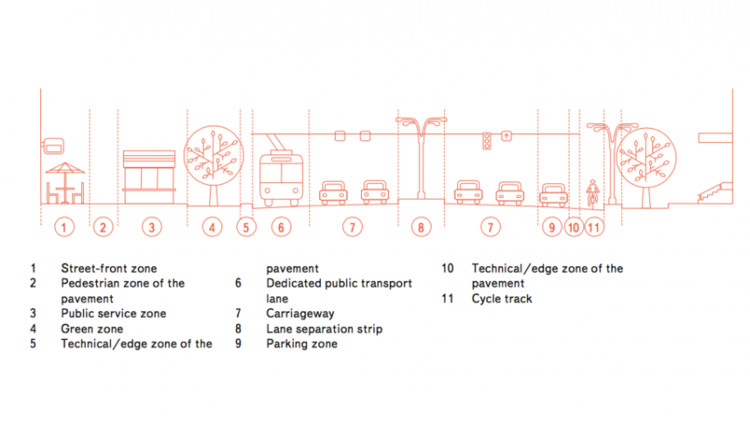
After we identified these ten street types, we started working on defining the best way to approach the development of each. The second book describes what a street of each type must have. We developed a general profile and functional zoning for each type. The pavement is more than just a pedestrian lane: there is a buffer zone between the roadway and the walking lane where the parking posts, street lights and communication lines are located. It’s a mandatory utility zone that has to be paved in such a way that any section can be easily unpaved and replaced. There is also a pedestrian fast lane for people walking to their workplace and a promenade with benches and other objects. Building façades have a large impact on the street they are facing. Restaurants and shops are located in these buildings. Making the adjacent zone retail-friendly is important. Cafes and restaurants must be able to open street patios to attract customers without disrupting the pedestrian traffic. How to apply these concepts to each of the street types is thoroughly explained in the Standard.
The third book describes eleven groups of design elements, including surface materials, benches, trash bins and lights. This catalogue of elements contains no mention of suppliers. It does not promote any manufacturers; instead it describes the attributes which define a quality product. For instance, the third book explains which type of tree grates will serve the longest while causing no damage to the root system of a tree. Styles of grates, bins, benches and other elements may vary, but all the items must comply with the quality standard.
Finally, the fourth book focuses on the planning process: how to perform preliminary analysis, how to apply user opinions during the development and how to achieve quality implementation. Additionally, there is a special emphasis on the fact that street planning cannot be carried out without any regard for the context of the street. A street should be regarded as a part of an interconnected system of various public spaces, together with adjacent parks, garden squares, yards and plazas.
Does the Standard have an official status? Should it be considered a law or merely a guideline?
There are a number of state-level laws and regulations relevant to street design issued by the Moscow Government. They were taken into account during the development of the manual. These regulations ensure safety standards and must be complied with. While the existing legislation covers safety aspects, our books introduce comfort standards. The Standard is basically a non-binding, advisory guideline created with the goal of improving the urban environment everywhere across the capital and maintaining it at a high level.
What happens if a street does not fit any of the mentioned types (and is not as significant as Tverskaya)? For instance, what if a street located in the New Moscow territory has cottages on one side, apartment complexes on the other and an entrance to the Moscow Ring Road somewhere along the way?
A standard is not a ready-made solution. The streets share common features yet also retain their individual attributes at the same time. Applying a single standard profile to every street is impossible. Adjustments are always in order.
The Standard offers three sets of solutions for each type of street with a large potential for combining various elements. The manual basically offers a convenient database that a designer working with a new space could use. That does not mean that all the new projects will look exactly the same. Some solutions featured in the Standard are yet to be implemented anywhere in Moscow. For instance, our collaboration with Transsolar, a German company consulting us on environmental comfort, revealed that Moscow’s largest environmental problem was not in fact CO2, but small-particle dust produced by studded tyre traction. And a simple method to control this type of pollution already exists. Many busy streets outside the city center have a green buffer zone separating the roadway from the sidewalks. A 1.5m high ground elevation running along this zone could filter out up to 70% of the tyre dust, preventing it from spreading into the residential areas. Western countries have been successfully using this technology for many years. Now it is a part of Moscow Standard. By the way, a terrain elevation could also help reduce the level of road noise.
.jpg?1471881026)
Does the Standard offer anything for the main roads? For example, nowadays Leningradskoye Highway basically splits the city into two disconnected parts; it’s a car dominion.
The Standard does not offer solutions for transportation problems. When we were defining our street typology, we relied on traffic load data calculated using Moscow’s transportation model. We pursued a goal of only offering solutions that would not aggravate the current transport situation. Any planned sidewalk extension or addition of a bicycle lane or road crossing should first be approved by the Moscow Department of Transport.
As for the main roads, our research revealed that the streets with the highest traffic load also have the heaviest pedestrian traffic. One would think that it should be the other way around. However, the main roads have metro stations, which generate a lot of pedestrian traffic, which in turn draws retail. Treating main roads the same way as highways is impossible. The needs of both vehicle traffic and local residents must be taken into account, which creates a paradox.
These territories have every opportunity to become more comfortable. Some have relatively large green buffer zones that currently remain underused. The Standard proposes to augment these zones with additional functionality. On one hand, some of the main streets will gain attraction centers, especially near intersections connecting them to the adjacent residential areas. Weekend markets are one example of such centers. On the other hand, the Standard involves the creation of zones able to absorb extra precipitation flowing from the roads and filter it. There is a list with types of vegetation best fit to handle this task. The same zones could be used to store snow in the winter. The meltwater will be naturally absorbed by the soil, alleviating the need for moving the snow out to melt. This, however, would require decreasing the quantity of melting chemicals sprayed over the snow, as the plants underneath might be susceptible to their effects.

Can the new Standard rid us of green lawn fences, yellow curbs and other eternal eyesores?
The choice of yellow and green appears random, so we have no idea how to actually fight that. The Standard offers no colour schemes. As long as fences meet the set requirements, their colour does not matter. However, currently they seem to fail to comply. The Standard states that lawns do not require fencing. This is a waste of materials: people will not trample grass and bushes just for the sake of it, while dog owners will trespass anyway. There are many other options for protecting lawns from being trampled. For instance, a same-level pavement strip with a different texture could protect a lawn from accidental intruders just as well as a curb can.
Natural soil water absorption is currently largely ignored, with most precipitation going down the storm drains. Meanwhile patches of open terrain on a street are able to absorb water. Employing these natural cycles in street layout could save resources.
Does the Standard provide any financial estimations? For instance, an approximate cost of renovating a street of a particular type?
No, as the Standard does not list any products of any particular brand, there are no prices to refer to. Nonetheless, the Standard was developed to fit three potential price ranges. Whether their estimated price is low or high, all the elements ensure that quality requirements are met. The same quality level must be maintained across the whole city and never drop below the set standard.

Let’s say a world-famous architect arrives to Moscow to design a street. He puts incredibly beautiful things into his project, which, unfortunately, contradict the Standard and are not guaranteed to work as intended. In that scenario, will the architect be told to stick to the Standard?
This could happen and I think it would be a good thing. If an architect plans to place a sculpture on a 1.5 meter wide sidewalk, would that really be a good idea? Following the Standard ensures smooth movement. Its goal is to reinvigorate the streets. In Copenhagen, new design manuals helped increase average time spent by residents outside by 20% over 10 years. That was achieved through creating convenient and attractive public spaces. Moreover, implementation of the Standard enables the creation of professional documentation for architects, which excludes the possibility of any instructions that will later be unclear to the experts trying to work with them. Finally, the Standard also pursues the task of providing the opportunity for the development of street retail.
Isn’t retail a whole different story? How can retail be introduced in such places as Strogino District, where the ground floors are living floors and have security bars on windows? By reintroducing street vendors?
True, business has no direct relation to street renovation. However, there is a strong connection between them. In Strogino, building façades are mostly located far from the sidewalk. Moreover, facades are often concealed by shrubbery and trees, making local businesses even less noticeable. Another problem is that first floor apartments cannot be used for commercial purposes due to insufficient ceiling height (3 m compared to 3.5 m required minimum). Nonetheless, we discovered multiple examples of shop owners reconstructing apartments in residential districts to meet the requirements.
Our British consultant Phil Wren, a street retail expert, travelled Moscow’s residential districts and studied the existing examples. He came up with a great idea: building an expansion connected to the façade and facing the sidewalk. This makes it possible both to achieve the required ceiling height and increase the visibility of the business to the passers-by. The part of the shop located in the apartment can be used as a utility room or a stockroom. This way the noise level is reduced, regulations are met and store space is increased. Our Russian consultants confirmed the viability of the proposed concept. And the Standard will ensure that any added expansions will look presentable.

Does the Standard also regulate façade appearances, an architectural element? What should be expected from this? It is unlikely that all houses which fail to comply will be demolished once the Standard is implemented.
Renovation works with what is given. Of course, façades cannot be changed. Central Moscow has a problem with mansions and many other buildings being fenced off, which prevents them from accommodating street retail. Central streets are also relatively narrow. The Standard proposes sidewalk expansion wherever the access to the first floors is open. Street renovation does not always involve planting trees. Some places require enhanced crossings so that people can quickly reach the other side of the street to get to a shop or a café. Those streets where the facades are windowless are a more suitable place to plant more vegetation.
Can an average person – not an architect, designer or construction worker – understand the new Standard, or is it a technical document which can only be interpreted by a professional?
Any person can. The Standard is written in a way that both professionals and common citizens are able to understand. The Standard contains multiple images, photos, infographics and diagrams and is written in plain language. We would love for more people to read it: the books contain many interesting solutions for our city that affect every pedestrian.
In late March it was revealed that Strelka KB would be developing a standard for recreational zones and public areas in Moscow. What differences will that document have from the Street Design Standard?
The two standards will have a lot in common. The city currently faces a task of developing a connected system of public spaces. The first logical step was to work with the streets which actually connect areas of attraction and other public spaces. Now the work on all other public spaces takes off. Parks, garden squares, yards, water bank recreation areas, plazas near metro stations must all fall into place. Work with these territories will set a single quality standard. In addition, it will improve Moscow’s quality of life and reduce air pollution. Simple solutions could improve airflow, increase biodiversity and reduce noise levels at the same time.
The renovation program is quite long and depends on numerous standards and documents. But when exactly will the endless repair works end? Are there any time estimations for when all these concepts will finally get implemented?
This is not an easy question. Full renovation may last decades. The Standard is the first step towards actually controlling the renovation process and its timeline. Until now renovation has been proceeding rather haphazardly. Now the city has decided that the way the streets are designed should be clarified. We understand that the Standard cannot last unchanged for eternity and should, just like any regulation, undergo periodical updates. The Standard uses flexible typology: a street of one type could transition to another within a few years under certain conditions, such as changes in its usage and its user categories. Everything must stay regularly updated according to the accumulated experience.
During our work on the Standard, we held regular roundtables joined by experts and ordinary citizens. One of our guests mentioned that he had recently started paying attention to Moscow’s facades, their beauty and their drawbacks. He was able to do that because he no longer had to watch his step. So the process has already started and we already see some results.

